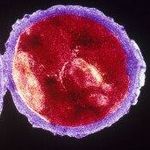
P acnes (Propionibacteria)
The provisional P.acnes MLST scheme uses internal fragments from 9 housekeeping genes spread around the genome;
lac (L-lactate dehydrogenase)
cob (Cobalamin biosynthesis CobD/CbiB protein)
oxc (Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II)
coa (O-succinylbenzoate-CoA synthase)
zno (Zn-dependant alcohol dehydrogenase)
gms (Glutamyl-tRNA synthetase)
pak (Pantothenate kinase)
fba (Fructose bisphosphate aldolase)
cel (Transcription regulator CelR)
PCR Conditions:
There are 3 different annealing temperatures to cover the amplification conditions of the 9 provisional PCR targets. As the final scheme is refined and finalised 1 annealing temperature may cover all targets. PCR amplification is carried out on chromosomal DNA using an extension time of 30 seconds, and an annealing temperature of 50C1, 52C2 or 55C3, with Qiagen Taq polymerase. This is repeated for 34 cycles. As the same primers are used for amplification and sequencing, it is important that only a single DNA fragment is amplified in the initial PCR. This may involve some optimisation of the annealing temperature.
1 – cob (primers at 50pmol/mL concentration).
2 – Annealing temperature of lac, oxc, fba.
3 – Annealing temperature of coa, zno, gls, pak, and cel.
The primer sequences for each PCR are;
cob up – 5’ CGA CGC CGC CGA GAT AG 3’
cob dn – 5’ TCA GGC CGC CGT AGA ACA 3’
lac up – 5’ GCC GCA GCC TTG GGA CTC T 3’
lac dn – 5’ GAA ATG CTG TCG CCC CGT G 3’
oxc up – 5’ GTG CTG CCG GAA AAG TCG 3’
oxc dn – 5’ CAC CGG CGT CAG GAT TGT 3’
fba up – 5’ AGG ACC CGC TAT TTC AAC TCT CA 3’
fba dn – 5’ ACG CGG GTC GTA CAT CTT CTT 3’
coa up – 5’ GCG GGA ATC GAG GGT GCT A 3’
coa dn – 5’ AGG GCC GCC GCT AGA TAA GTA 3’
zno up – 5’ CGC CGG CAT CAC CAC CTA TT 3’
zno dn – 5’ TCT CAC ATC GCC CGC AAC C 3’
gls up – 5’ CCG CCT CAC CGT CCA GCA 3’
gls dn – 5’ CAC ATC GAG AAC CGC ATC ACTC 3’
pak up – 5’ CGACGC CTC CAA TAA CTT CC 3’
pak dn – 5’ GTC GGC CTC CTC AGC ATC 3’
cel up – 5’ GCC GAC GTT TTC TAC AGT GAG C 3’
cel dn – 5’ GGC GGT GAG GGT CCA TTC A 3’
For further information please contact Simon O’Hanlon
Propionibacteria acnes (lat. Propionibacterium) is a strain of gram-positive facultative anaerobic immobilized bacteria that synthesize propionic acid in the process of metabolism. Propionibacterium usually has the form of sharp sticks. Its size is about 0.5-0.8 per 1.0-1.5 μм. Less often, it is curved or club-shaped depending on the conditions and development cycle. Propionibacterium reproduces by binary fission. It does not form spores.
Propionibacterium acnes are the causative agents of propionic acid fermentation, in which carbohydrates are formed with the main fermentation products – propionic acid and its salts – propionates. Propionic acid fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation when lactic acid bacteria (lactobacilli, streptococci and other representatives of the Lactobacillales order) convert lactose, glucose and other carbohydrates into lactic acid. In addition to propionic acid, propionic acid bacteria produce acetic acid, carbon dioxide, etc.
Propionibacterium does not inhabit soil and water bodies. They are found in the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants and are often found in dairy products. The process of milk fermentation with propionibacteria is rather slow lasting for 5-7 days.
Most propionibacteria cannot reproduce when the medium pH is less than 5.0–4.5. Propionibacterium only tolerates low oxygen partial pressures. The optimum temperature is 30–35 °С, at a temperature of 60–70 °С these bacteria die. Propionibacterium, in addition to sugars and lactic acid, is able to convert pyruvic acid, glycerin, and other substances. They dissolve amino acids, as a result of which fatty acids are released.
A number of Propionibacterium species are capable of producing vitamin B12. These quality propionibacteria are used in vitamins’ production.
P acnes bacteria in the human body
Some species of P acnes bacteria inhabit the skin of humans and other animals. They are located mainly around the sweat glands, sebaceous glands and other areas of the skin. It is considered to be one of the most common microorganisms on human skin. Propionibacteria are the predominant bacteria in the so-called “oily” areas of the skin. Propionibacterium is also present in the human colon.
Can propionic acid bacteria cause diseases?
In most people, propionic acid bacteria usually do not cause any health problems. Human diseases are caused only by some of the types of propionic acid bacteria that live on human skin.
Acne is caused by Propionibacterium acnes. The species Propionibacterium acnes is one of the most common infectious forms of acne, a disease of the sebaceous glands. In addition, Propionibacterium acnes can cause blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids), endophthalmitis (purulent inflammation of the inner membranes of the eyeball), and other eye diseases, in particular, complications after ophthalmic surgery.
Antibiotics active against propionic acid bacteria
Antibacterial agents (those described in this reference) that are active against Propionibacterium: clarithromycin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, clindamycin.